The figure given below shows the cost and revenue curves of a monopolist.Figure 11.9
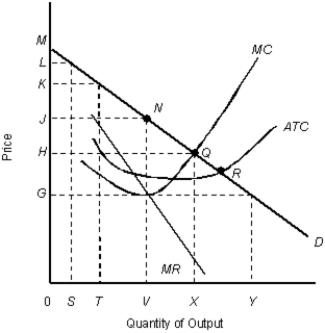 D: Average revenue
D: Average revenue
MR: Marginal revenue
ATC: Average total cost
MC: Marginal cost
-Economies of scale, control over a scarce input, and patents are all examples of barriers to entry.
Definitions:
Proteins
Large biomolecules consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues, essential for the structure, function, and regulation of the body's tissues and organs.
Amino Acids
Organic compounds that combine to form proteins and are known as the building blocks of life, essential for various bodily functions.
Double Covalent
A type of chemical bond where two pairs of electrons are shared between two atoms for a stronger bond.
Single Covalent
A type of chemical bond where two atoms share one pair of valence electrons.
Q23: When a particular resource is commonly used,
Q26: When practicing price discrimination, a firm can
Q29: In a natural monopoly, government regulation is
Q44: Refer to Table 9.2. If we assume
Q63: Under a marketable pollution permit system, property
Q74: If the total cost of producing 6
Q82: According to economic theory, the difference between
Q106: The theory of bounded rationality states that
Q107: Which among the following does not determine
Q130: Suppose that apples and bananas both cost