The figure given below shows the cost and revenue curves of a monopolist.Figure 11.9
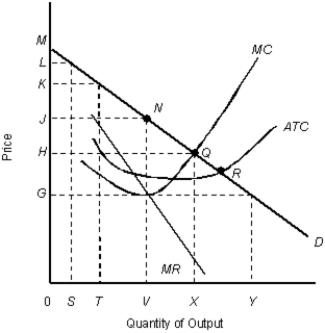 D: Average revenue
D: Average revenue
MR: Marginal revenue
ATC: Average total cost
MC: Marginal cost
-A monopolist can charge whatever price it wants and can therefore reap phenomenal profits.
Definitions:
Business Combination
A transaction where two or more entities come together to form a consolidated enterprise through mergers, acquisitions, or other forms of corporate restructuring.
Moratorium Statutes
Laws that temporarily prohibit certain actions or suspend certain rights, often during emergencies or crises, to provide relief or prevent harm.
Tender Offers
A proposal by an entity or individual to purchase shares from the shareholders of a company at a specific price for a certain period.
Section 16(a)
A provision often found in legal documents that specifies particular regulations or requirements, the exact meaning depends on the context of the document.
Q3: Given the same unit costs, a monopolist
Q10: One of the reasons that communism failed
Q19: A firm's accounting profit is called a
Q33: A perfectly competitive producer's demand curve is:<br>A)a
Q43: If a resource can be put to
Q60: The most-favored customer is one who:<br>A)buys a
Q98: Diseconomies of scale:<br>A)occur only in the short
Q107: According to Table 14.1, the marginal revenue
Q123: Consumer equilibrium exists when the marginal utility
Q139: The law of diminishing marginal utility states