The figure given below shows the cost and revenue curves of a monopolist.Figure 11.9
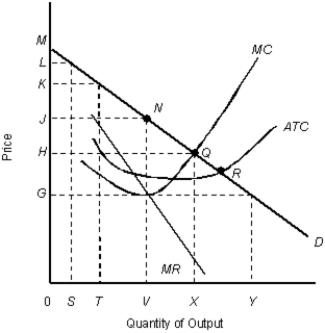 D: Average revenue
D: Average revenue
MR: Marginal revenue
ATC: Average total cost
MC: Marginal cost
-If a monopolist is producing at that output where price equals average variable cost in the short run, then it is earning a negative profit.
Definitions:
Machine-Hours
A measure of the amount of time machines are used in the production process, often utilized as an allocation base for applying overhead costs to products.
Unit Product Costs
The total cost associated with producing one unit of a product, including direct materials, direct labor, and overhead.
Markup
The difference between the cost of a good or service and its selling price, expressed as a percentage over the cost.
Selling Price
Selling price is the amount at which a product or service is offered to consumers, calculated to cover costs, overheads, and profit.
Q3: The good for which neither the principle
Q12: One reason that monopolistically competitive firms often
Q23: Which of the following practices is not
Q34: In Figure 7.3, the consumer is in
Q52: In the United States, monopoly regulation began
Q60: Which of the following calculations is necessary
Q82: A firm will always maximize profit at
Q83: According to Figure 16.2, assume that the
Q88: A monopolist enjoys the least market power
Q89: If a firm hires its fourth worker