The figure given below shows the cost and revenue curves of a monopolist.Figure 11.9
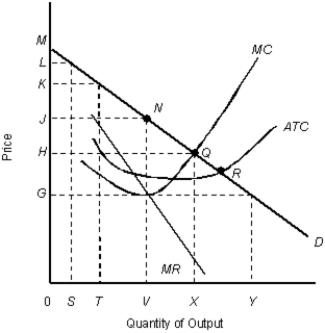 D: Average revenue
D: Average revenue
MR: Marginal revenue
ATC: Average total cost
MC: Marginal cost
-Monopolistic competition is similar to perfect competition in that:
Definitions:
Net Operating Income
The total profit of a company after operating expenses are subtracted from operating revenues but before incomes and taxes are accounted for.
Total Common Corporate Costs
The aggregate of all expenses shared across departments within a corporation, not directly attributed to specific departments or products.
Contribution Margin
The difference between a company's total sales revenue and its variable costs.
Fixed Costs
Expenses that remain constant for a certain level of production or period, inclusive of rent, salaries, and insurance.
Q11: A monopolist's demand curve is less elastic
Q18: A positively sloped long run average cost
Q21: A deadweight loss arises under perfect competition.
Q32: If a firm doubles its resources and
Q49: From a social viewpoint, when price =
Q49: A cartel attempts to increase profits in
Q57: When regulating a natural monopoly, government officials
Q91: A monopolistically competitive firm's demand curve slopes
Q99: The addition to a business firm's total
Q106: The theory of bounded rationality states that