In the following figure, the first panel shows a market situation prior to regulation and the second panel shows the effects of regulation.Figure 14.2
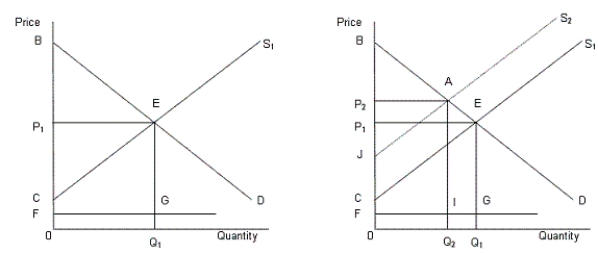 In the figure,
In the figure,
D: Demand curve for automobiles
S1: Supply curve of automobiles prior to regulation
S2: Supply curve of automobiles after regulation
FG: Clean up cost per unit
-Any kind of social regulation raises the per unit cost of production of a good and hence leads to a loss of producer and consumer surplus.
Definitions:
Receivables
Amounts due to a company for goods or services that have been provided but not yet paid for by the customers.
Accrue Expenses
The recording of expenses that have been incurred but not yet paid, reflecting obligations on the balance sheet.
Indirect Method
A way of preparing the cash flow statement where net income is adjusted for non-cash transactions, deferred taxes, and changes in working capital to calculate cash flow from operating activities.
Depreciation Expense
An accounting method of allocating the cost of a tangible asset over its useful life to account for declines in value over time.
Q2: When consumers have perfect information about the
Q5: In Figure 18.1, the curve B indicates:<br>A)supply
Q14: Per capita income is calculated as:<br>A)national income
Q19: In the long-run, in a monopolistically competitive
Q28: The theory of the long-run in perfect
Q38: In China prior to 1990, most residential
Q69: Firms in monopolistically competitive markets spend significant
Q85: Education is a good example of a
Q104: Which of the following factors is likely
Q105: Perfect competition is the only market structure