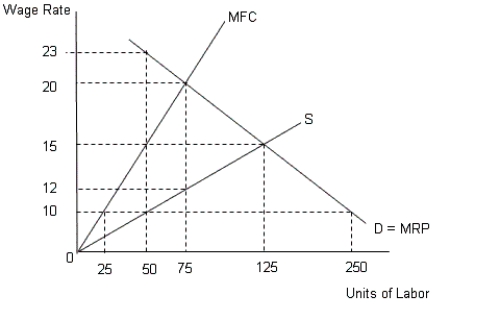
The figure given below represents equilibrium in the labor market with the demand and supply curves of labor.Figure 14.6
In the figure,
D = MRP implies demand for labor = Marginal Revenue Product
MFC represents Marginal Factor Cost curve
S represents the supply curve of labor
-An individual purchasing goods and services will allocate his expenditures so that the pleasure he gets out of spending one more dollar is the same no matter what he spends that dollar on. For a firm purchasing resources, this is the same as ensuring that:
Definitions:
Inductive Step
A critical process in mathematical induction where one proves that if a statement holds for one natural number, it holds for the next number as well.
Hypothetical Syllogism
A form of logical argument involving two conditional statements and a conclusion derived from them.
Modus Ponens
A form of logical argument where if a conditional statement ("if P then Q") is accepted, and the antecedent (P) holds, then the consequent (Q) can be concluded.
Inductive Generalization
A form of reasoning where a conclusion is drawn about all members of a group based on observations of a sample of that group.
Q15: The phrase, "Google stock soared Friday, continuing
Q29: According to Table 20.4, the limits to
Q32: When negative externalities exist in production, _.<br>A)the
Q39: Production becomes more efficient if a common
Q39: If everyone had the same income, then
Q51: Income inequality is indicated by a Lorenz
Q52: When the government tries to control pollution
Q67: Which of the following raises the economic
Q89: According to Table 20.4, the limits to
Q118: Consider the monopolist described in the Figure