Exhibit 4.1
The following questions are based on the problem below and accompanying Analytic Solver Platform sensitivity report.
Carlton construction is supplying building materials for a new mall construction project in Kansas. Their contract calls for a total of 250,000 tons of material to be delivered over a three-week period. Carlton's supply depot has access to three modes of transportation: a trucking fleet, railway delivery, and air cargo transport. Their contract calls for 120,000 tons delivered by the end of week one, 80% of the total delivered by the end of week two, and the entire amount delivered by the end of week three. Contracts in place with the transportation companies call for at least 45% of the total delivered be delivered by trucking, at least 40% of the total delivered be delivered by railway, and up to 15% of the total delivered be delivered by air cargo. Unfortunately, competing demands limit the availability of each mode of transportation each of the three weeks to the following levels (all in thousands of tons): 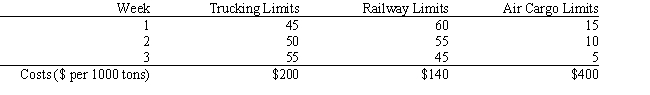 The following is the LP model for this logistics problem.
The following is the LP model for this logistics problem. 
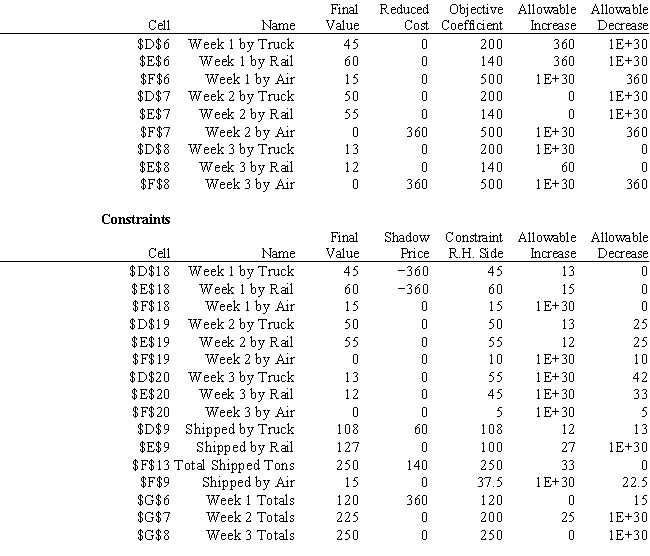
-Refer to Exhibit 4.1. Should the company negotiate for additional air delivery capacity?
Definitions:
Democratic Party
One of the two major contemporary political parties in the United States, traditionally associated with progressive and liberal policies.
Fifteenth Amendment
An amendment to the United States Constitution, ratified in 1870, that prohibits the federal government and each state from denying a citizen the right to vote based on that citizen's "race, color, or previous condition of servitude."
Democratic State Primaries
A process by which the Democratic Party in the United States selects its candidates for various elected positions in government.
Smith V. Allwright
A landmark 1944 US Supreme Court decision that ended the practice of "white primaries" by declaring it unconstitutional, thus allowing African Americans to vote in primary elections.
Q17: Bob and Dora Sweet wish to start
Q38: Refer to Exhibit 10.1.What percentage of the
Q40: Refer to Exhibit 3.2.Which cells should be
Q44: The indirect costs of disclosure involve the<br>A)
Q48: The difference between the right-hand side RHS)values
Q51: A small town wants to build
Q52: Solve the following LP problem graphically by
Q57: The constraint for resource 1 is 5
Q79: If a company produces Product 1,then it
Q84: The following network depicts a balanced transportation/distribution