Table 2-26
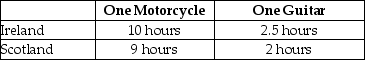
-Refer to Table 2-26. This table shows the number of labor hours required to produce a motorcycle and a guitar in Ireland and Scotland.
a. If each country has a total of 2,700 labor hours to devote to the production of the two goods, draw the production possibilities frontier for each country. Put "Motorcycle" on the horizontal axis and "Guitar" on the vertical axis. Be sure to identify the intercept values on your graphs.
b. Suppose each country allocates 55% its labor hours to guitar production and 45% to the production of motorcycles. Complete Table 2-27 below to show each country's output of the two products.
Table 2-27: Production and Consumption with no Trade
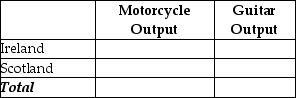 c. If the two countries do not trade and consume whatever they produce, identify the current production and consumption point for each country on their respective production possibilities frontiers. Label Ireland's consumption point "I" and Scotland's consumption point, "S."
c. If the two countries do not trade and consume whatever they produce, identify the current production and consumption point for each country on their respective production possibilities frontiers. Label Ireland's consumption point "I" and Scotland's consumption point, "S."
d. Suppose the two countries specialize and trade. Who should produce motorcycles and who should produce guitars? Explain your answer.
e. Complete Table 2-28 below to show each country's output with specialization.
Table 2-28: Output with Specialization
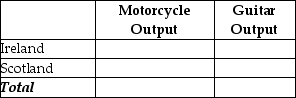 f. Did specialization increase the combined output for the two countries without any increase in resources? If so, by how much?
f. Did specialization increase the combined output for the two countries without any increase in resources? If so, by how much?
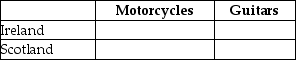
g. Suppose Ireland and Scotland agree to trade so that in exchange for 600 guitars, the exporter of guitars receives 140 motorcycles. Complete Table 2-29 below to show each country's consumption bundle after trade.
Table 2-29: Consumption with Trade
 h. Show the consumption points after trade on each country's production possibilities frontier. Label these points "X" for Ireland and "Y" for Scotland.
h. Show the consumption points after trade on each country's production possibilities frontier. Label these points "X" for Ireland and "Y" for Scotland.
i. Has trade made the two countries better off? Explain your answer.
Definitions:
Marketing Spending
The total expenditure by a company on marketing activities, including advertising, promotions, and other strategies to increase sales.
Primary Target Market
The specific group of consumers identified by a business as its main focus for marketing efforts, based on shared characteristics or needs.
On-the-Go Women
Refers to products or services specifically designed or marketed to meet the needs of women with busy lifestyles.
Strategic Marketing Process
The approach taken by an organization to align marketing strategies with its overall goals, involving planning, execution, and evaluation.
Q36: Gross domestic product understates the total production
Q37: If the nominal interest rate is 6%
Q51: The government of Silverado raises revenue through
Q89: If real GDP increases we know for
Q167: A final good is one that<br>A) is
Q193: In comparing China to Canada, China's relatively
Q227: Individuals who have never been the best
Q320: Refer to Table 2-16. What is Finland's
Q356: In the circular flow model, producers<br>A) sell
Q405: If property rights are not well enforced,