Use the information below to answer the following question(s) .
Crabtree Ornaments Company uses job costing. Crabtree Ornaments Company has two departments, Trimming and Finishing. Manufacturing overhead is allocated based on direct labour cost in the Trimming Department and direct labour hours in the Finishing Department. The following additional information is available:
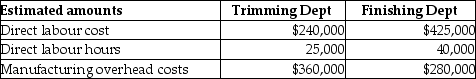
Actual data for completed Job No. 650 is as follows:
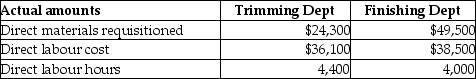
-What is the predetermined manufacturing overhead rate for the Finishing Department at Crabtree Ornaments Company?
Definitions:
Individual Demand Curves
Graphical representations showing the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity demanded by an individual consumer, holding other factors constant.
Public Goods
Goods that are non-excludable and non-rivalrous, meaning they can be used by anyone and one person's use does not reduce its availability to others.
Free-Rider Problem
A situation where individuals consume a public good without contributing to its cost, benefiting from the good without paying for it.
Samuelson's Theory
Refers to economist Paul Samuelson's contributions to economic theory, including insights on public goods, trade, and welfare economics.
Q44: How many people must purchase tickets assuming
Q48: The sales mix can greatly affect CVP
Q50: Inspection is considered a value-added activity.
Q52: What is the predetermined overhead rate for
Q108: The Laramie Factory produces expensive boots. It
Q142: The Settler's Chuck Wagon sells tickets for
Q145: Value-added activities can be described as activities
Q206: If Job No. 650 consists of 500
Q235: In process costing the Work in Process
Q344: Management can use the job cost information