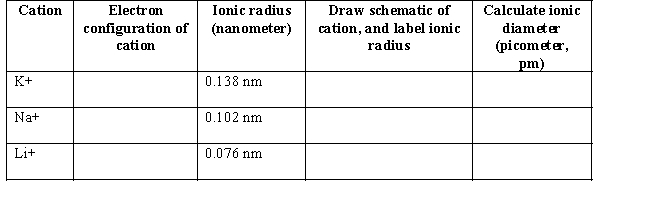
(a) Group I cations are common ions found in organic salts.Write the electron configuration for the Group I cations below.In the fourth column,use circles to represent the relative size of each cation conceptually.Define the term ionic radius and label the ionic radius of each cation.
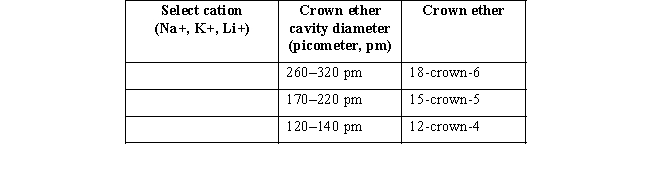
(b) Organic molecules called crown ethers (refer to the box titled "Phase Transfer Catalysts" in Chapter 2 of your text)can sequester a cation of specific size to make the organic anion more reactive.Charles Pedersen,in fact,shared the 1987 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for contributions to the synthesis of crown ethers.Suppose you wanted to use a crown ether to selectively remove each individual cation from a solution of sodium,lithium,and potassium.For each cation,which crown ether might you add?
Definitions:
Antagonist
A muscle that opposes the action of another muscle, known as the agonist, to enable movement and coordination.
Flexion
A movement that decreases the angle between two body parts, such as bending the arm at the elbow.
Lower Limb
Refers to the portion of the body from the hip to the toes, including the thigh, leg, ankle, and foot.
Posterior Side
The back or rear part of the body or an object, opposite of anterior.
Q2: What are the approximate H<font face="symbol"></font>C<font face="symbol"></font>H
Q18: Which of the following functional groups contains
Q20: Draw six constitutional isomers for C<sub>4</sub>H<sub>11</sub>N.
Q24: Accounting procedures for all items are the
Q36: Which of the following isomers is most
Q46: What is the conjugate base for phenol
Q50: Which of the following is a diastereomer
Q55: What is the most likely product of
Q68: Partner return on equity is calculated as
Q166: _ refers to all changes in equity