A local parent group was concerned with the increasing school cost for families with school aged children.The parent group was interested in understanding the relationship between the
The academic grade level for the child and the total costs spent per child per academic year.They
Performed a multiple regression analysis using total cost as the dependent variable and academic
Year (x1) as the independent variables.The multiple regression analysis produced the following
Tables.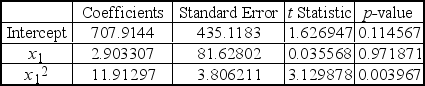
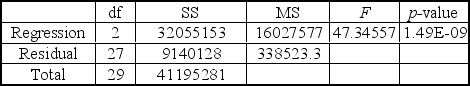
Using = 0.05 to test the null hypothesis H0: 2 = 0,the critical t value is ____.
Definitions:
Joint Probability Distribution
A statistical measure that gives the probability of two events occurring together and at the same point in time.
Discrete Random Variables
Variables that assume a finite or countably infinite set of values, each with a certain probability.
P(X = x, Y = y)
The joint probability of two discrete random variables X and Y taking on specific values x and y, respectively.
Uniform Distribution
A type of probability distribution where all outcomes are equally likely to occur within a defined range.
Q7: The F-value to test the overall significance
Q25: The regression model y =
Q25: The motivation for using an index number
Q27: A researcher wants to determine the efficacy
Q31: Suppose that the regression equation y =
Q49: Collinsville Construction Company purchases steel rods
Q58: Elwin Osbourne,CIO at GFS,Inc.,suspects that at least
Q75: Inspection of the following table of correlation
Q76: A researcher wants to study the effects
Q105: The coefficient of correlation in a simple