The monthly cost of driving a car depends on the number of miles driven.Julia found that in October it cost her 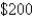 to drive
to drive 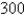 mi and in July it cost her
mi and in July it cost her 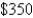 to drive
to drive 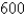 mi.Express the monthly cost C as a function of the distance driven d assuming that a linear relationship gives a suitable model.
mi.Express the monthly cost C as a function of the distance driven d assuming that a linear relationship gives a suitable model.
Definitions:
Commandments of Listening
Fundamental principles or rules that emphasize the importance and techniques of effective listening.
Frequently Asking Questions
A list of queries that are often posed by individuals, used to address common concerns or clarify information.
Talker's Ability
The skill or proficiency of an individual in conveying information, emotions, or ideas through speech.
Parliamentary Procedure
A set of rules for conduct at meetings, intended to ensure smooth proceedings through orderly and efficient processes.
Q1: Sketch the region bounded by the graphs
Q1: Find the derivative of the vector function.
Q2: Find the solution of the differential equation
Q3: Which of the following is true of
Q3: The developing area receiving the largest share
Q4: The long-run social benefits of infant industry
Q7: Even though greatly diminished in market share
Q8: Use the graph of the function to
Q9: Which of the following is true about
Q12: A construction loan can include all of