One model for the spread of an epidemic is that the rate of spread is jointly proportional to the number of infected people and the number of uninfected people.In an isolated town of 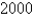 inhabitants,
inhabitants, 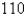 people have a disease at the beginning of the week and
people have a disease at the beginning of the week and 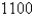 have it at the end of the week.How long does it take for
have it at the end of the week.How long does it take for 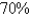 of the population to be infected?
of the population to be infected?
Definitions:
Extracellular
Pertaining to being outside the cell membrane.
Plasma Membrane
A biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment, controlling the movement of substances in and out of cells.
Permeable
A characteristic of materials that are able to allow liquids or gases to pass through them, especially through pores or interstices.
Gray Matter
The darker-colored area of the central nervous system; abundant in nerve cell bodies, dendrites, and axon terminals, associated with processing and cognition.
Q2: The curve with the equation <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6897/.jpg"
Q4: Estimate the value of the following limit
Q4: Identify the surface with equation <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6897/.jpg"
Q4: The relationship between the Fahrenheit and Celsius
Q5: The Bankruptcy Abuse Prevention and Consumer Protection
Q7: A steady wind blows a kite due
Q9: Fiscal policies of the government can best
Q32: According to Marxist historians, in conflicts during
Q41: Typical police officers fire their weapon _
Q62: The Germans had the greatest influence in