Consider the following two equilibria and their respective equilibrium constants:
(1) NO(g) + 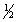
O2(g) 
NO2(g)
(2) 2NO2(g) 
2NO(g) + O2(g)
Which one of the following is the correct relationship between the equilibrium constants K1 and K2?
Definitions:
Unit Contribution Margin
The difference between the selling price per unit and the variable cost per unit, indicating how much each unit contributes to covering fixed costs and generating profit.
Break-Even Point
The production level at which total revenues equal total expenses, and there is neither profit nor loss.
Total Revenue
The total income generated from business activities before any expenses are subtracted.
Total Cost
Represents the complete amount of expenses incurred by a business in producing goods or services.
Q1: Once a reaction system reaches equilibrium,the concentrations
Q5: The density of pure water at 25°C
Q20: Which relationship or statement best describes
Q32: Cinnamaldehyde ( <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5832/.jpg" alt="Cinnamaldehyde (
Q33: The half-life of a second-order reaction does
Q47: Which of the following is true
Q57: An elementary reaction is a simple,one-step process.
Q60: The solubility of calcium chromate is
Q67: Which of the following will be paramagnetic?<br>A)V<sup>5+</sup><br>B)Ni<sup>2+</sup><br>C)Mn<sup>7+</sup><br>D)Ti<sup>4+</sup><br>E)Zn
Q73: A metal such as chromium in the