Consider the following two equilibria and their respective equilibrium constants:
(1) NO(g) + 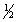
O2(g) 
NO2(g)
(2) 2NO2(g) 
2NO(g) + O2(g)
Which one of the following is the correct relationship between the equilibrium constants K1 and K2?
Definitions:
Overhead Allocated
Overhead Allocated refers to the process of distributing indirect costs (overheads) to specific cost objects, such as products or departments, based on a predetermined allocation method.
Contribution Per Machine Hour
A measure of profitability that calculates how much profit or contribution is generated for every machine hour used in production.
Target Costing
A pricing strategy where a product's sale price is determined first, and then the production cost is targeted to ensure profitability.
Market-Based Pricing
A pricing strategy where the selling price of a product or service is determined by the current market conditions, including demand, competition, and cost of production.
Q3: The reaction quotient for a gas phase
Q12: Predict the ideal bond angles in FNO
Q14: Which of the following aqueous solutions should
Q35: Predict the ideal bond angles in GeCl<sub>4</sub>
Q40: Boron has 3 valence electrons.Which of
Q49: The half-life of a first-order reaction does
Q54: The units of the rate constant depend
Q65: Consider the phase diagram shown below. <img
Q82: Hydrogen sulfide will react with water
Q88: (a)Write a balanced equation representing the reaction