A recent discovery has suggested that a gene mutation results in several amino acid substitutions within an active site.The following substitutions have been identified and are each expected to form the active site: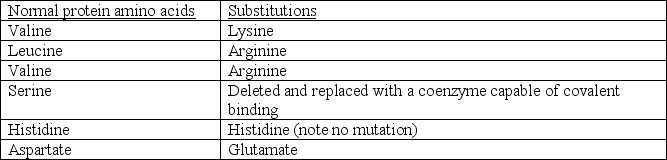
It was also noticed that a coenzyme molecule containing a hydroxyl (-OH) group binds to the mutated protein in approximately the same location as the original serine but does not alter the structure of the protein in anyway.Based on your knowledge of amino acids,enzymes,and catalysis,which of the following is a REASONABLE conclusion?
Definitions:
PGAL
Phosphoglyceraldehyde, a three-carbon molecule that is an important intermediate in the photosynthetic conversion of carbon dioxide into glucose as well as in glycolysis.
Phosphoglyceraldehyde
An intermediary compound in glycolysis and photosynthesis, playing a critical role in the metabolic pathways that generate energy and organic molecules.
Light-Dependent Reactions
These are the initial phase of photosynthesis, where light energy is captured and used to produce ATP and NADPH, which are necessary for the subsequent light-independent reactions.
Q1: Which of the following best describes the
Q3: After hybridization,the fragment of interest can be
Q19: Which of the following best describes the
Q23: Which of the following would decrease the
Q33: _ are bacterial proteins forming a
Q34: A release of _ would result in
Q38: What group is attached to the pyrimidine
Q56: Which of the following statements describes integral
Q62: Which of the following nucleotides contain energy
Q63: N-linked oligosaccharides can be covalently linked to