In the previous chapter you learned about why cartels are hard to maintain since cheating is a dominant strategy for all firms involved. If this table represents the payoffs for two firms operating as a cartel, are there any Nash equilibria in this coordination game? If so, how many? For these payoffs, what is the "best" equilibrium outcome for both firms? Which outcome is likely to occur in the market? Does your answer change if these firms can communicate and/or monitor each other easily? Explain.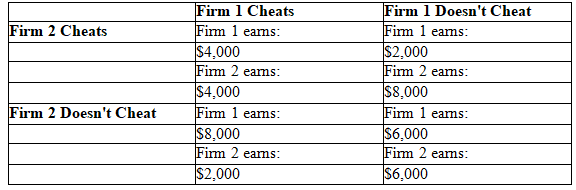
Definitions:
Sensorimotor Stage
The first of Jean Piaget's stages of cognitive development, where infants from birth to about 2 years old learn through interacting with their environment using their senses and motor actions.
Active Experimentation
A learning approach where individuals learn by doing, engaging in activities to test hypotheses and reflect on outcomes to gain new knowledge.
Mental Combinations
The process where children start to mentally link objects and ideas, indicative of early cognitive development.
Sensorimotor Stage
The first developmental stage in Piaget's theory of cognitive development, where infants learn about the world primarily through their senses and motor actions.
Q2: The two major types of discrimination are:<br>A)
Q13: If cable TV packages were unbundled, the
Q31: Which of the following is/are TRUE regarding
Q67: If Bob's wages _ and he works
Q81: Some current members of the military are
Q83: In general, wages are determined:<br>A) by the
Q94: Hewlett Packard's pricing scheme is to sell
Q148: Microsoft's market power stems from:<br>A) its control
Q158: Which statement is FALSE?<br>A) Network goods are
Q170: In an oligopolistic market, prices will tend