The financial statements for Goodwin, Inc., and Corr Company for the year ended December 31, 20X1, prior to Goodwin's acquisition business combination transaction regarding Corr, follow (in thousands) :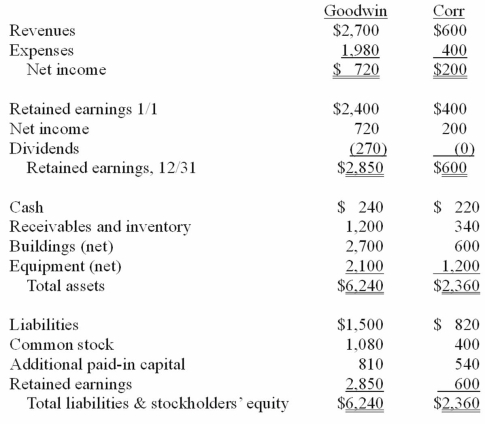
On December 31, 20X1, Goodwin issued $600 in debt and 30 shares of its $10 par value common stock to the owners of Corr to acquire all of the outstanding shares of that company. Goodwin shares had a fair value of $40 per share.
Goodwin paid $25 to a broker for arranging the transaction. Goodwin paid $35 in stock issuance costs. Corr's equipment was actually worth $1,400 but its buildings were only valued at $560.
Compute the consolidated buildings (net) account at December 31, 20X1.
Definitions:
Degree Of Operating Leverage
A financial ratio that measures the sensitivity of a company's operating income to its sales.
Contribution Format
A financial statement format that separates fixed costs from variable costs to highlight the contribution margin of products or services.
Margin of Safety
The difference between actual sales and the break-even point, used to evaluate the level of risk in a business operation.
Break-even Sales
The amount of revenue required to cover total fixed and variable costs, at which point a business neither makes a profit nor incurs a loss.
Q8: Pell Company acquires 80% of Demers Company
Q10: When an exoplanet passes in front of
Q16: Compared to today, in the future, the
Q20: Pell Company acquires 80% of Demers Company
Q27: Pell Company acquires 80% of Demers Company
Q35: In our search for stars with habitable
Q45: McGuire Company acquired 90 percent of Hogan
Q64: Suppose there are a million habitable planets
Q76: Encephalization Quotient (EQ) values can be estimated
Q99: On January 1, 2011, Pride, Inc. acquired