A portfolio manager in charge of a bank portfolio has $10 million to invest. The securities available for purchase, as well as their respective quality ratings, maturities, and yields, are shown in the table below:
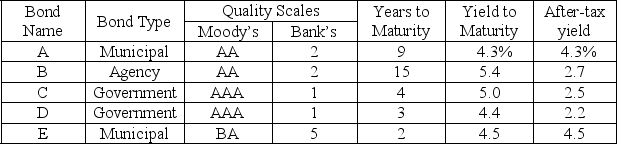
The bank places the following policy limitations on the portfolio manager's actions:
1. Government and agency bonds must total at least $4 million.
2. The average quality of the portfolio cannot exceed 1.4 on the bank's quality scale. (Note that a low number on this scale means a high-quality bond.)
3. The average years to maturity of the portfolio must not exceed 5 years.
Assuming that the objective of the portfolio manager is to maximize after-tax earnings and that the tax rate is 50%, formulate a linear program that can be used to determine how much money to invest in each type of bond.
Definitions:
Cash Flow
The net amount of cash and cash equivalents being transferred into and out of a business.
Par Value
The face value of a bond, stock, or coupon as stated by the issuer, which is the minimum amount at which the security can be sold.
Preferred Stock
A class of ownership in a corporation with a higher claim on assets and earnings than common stock, typically with dividends that are paid out before dividends to common shareholders.
No-par Common Stock
No-par common stock is issued without a par value, and its value is determined by what investors are willing to pay for it, rather than being stated in the company's charter.
Q7: Compare the access differences among the Internet,
Q36: Companies want a supply chain that makes
Q39: For an optimization problem a(an) _ violates
Q53: Suppose that weekly output is worth $1000,
Q88: Visitors to a major amusement park would
Q91: McDonald's and Pizzerias compete on the same
Q92: In Linear Programming models, what do you
Q97: Who created "scientific management?"<br>A) James Watt<br>B) Adam
Q120: In the Excel MATCH function, which argument
Q129: Which of the following historical figures would