Given the following data:
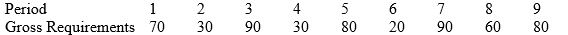
The beginning inventory is 0 and there are no scheduled receipts. The order cost is $90 and the holding cost is $1 per part per period.
(a) What are the order costs, carrying costs, and totals cost over the 9 periods using the lot-for-lot size rule?
(b) What are the order costs, carrying costs, and totals cost over the 9 periods using the fixed order quantity rule with FOQ = 100?
(c) What are the order costs, carrying costs, and totals cost over the 9 periods using the period order quantity rule with POQ = 3?
Definitions:
Species
An assembly of living entities which are alike in nature and have the ability to mate or share genes.
File Drawer
The phenomenon where only positive study results are published, while negative or inconclusive findings are "hidden" in a researcher's file drawer.
Genus
A class or group of entities that share common characteristics, often used in the classification of organisms.
Species
A basic rank of biological classification that involves groups of individuals capable of interbreeding to produce fertile offspring.
Q3: In 1970, the Public Health Service Act
Q6: Which of the following would constitute short
Q15: What department evaluates and certifies employee credentials
Q26: A blood bank technologist working in an
Q32: There are a limited number of options
Q38: Having waiters cook and having the cooks
Q45: The termination phase in the project life
Q49: The first unit of a product took
Q67: Jackie is the owner and the manager
Q100: What are small groups of employees who