Refer to the figure below. 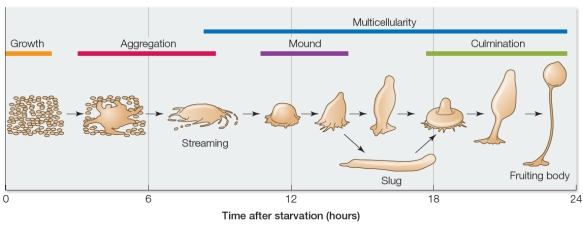 The diagram depicts the life cycle of an organism known as a slime mold, which can be found in temperate forest ecosystems.A slime mold begins as a group of single cells that function independently when nutrients are readily available.However, these cells begin aggregating to form a multicellular slug and then a fruiting body when starved.The fruiting body produces spores and dies after releasing the spores.Provided that they land in a nutrient-rich environment, spores then develop into individual cells that can begin the process over again.Using this information, explain how cell specialization contributes to the biological success of slime molds.
The diagram depicts the life cycle of an organism known as a slime mold, which can be found in temperate forest ecosystems.A slime mold begins as a group of single cells that function independently when nutrients are readily available.However, these cells begin aggregating to form a multicellular slug and then a fruiting body when starved.The fruiting body produces spores and dies after releasing the spores.Provided that they land in a nutrient-rich environment, spores then develop into individual cells that can begin the process over again.Using this information, explain how cell specialization contributes to the biological success of slime molds.
Definitions:
Stained Glass
Colored glass pieces assembled into patterns or pictures, often used in windows, to control light and enhance the beauty of buildings, especially in churches.
Tapestry
A weaving technique in which the weft threads are packed densely over the warp threads so that the designs are woven directly into the fabric.
Cross-Hatching
A drawing technique used to create shading and texture, consisting of intersecting sets of parallel lines.
Engraving
A printmaking process where designs are incised onto a hard surface, such as metal plates or wood blocks, to produce images on paper.
Q12: The nurse accesses previous hospitalization information to
Q16: The nurse reviews clients' records and the
Q20: Refer to the figures below. <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5650/.jpg"
Q22: A client complaining of "extreme" low back
Q26: A client with diabetes wants to have
Q46: Which six elements provide most of the
Q133: Which is not a direct concern for
Q143: Refer to the figure below. <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5650/.jpg"
Q194: Refer to the graph below showing the
Q227: The three major groups of multicellular eukaryotes