Refer to the graph below showing data collected from experiments performed on living leaves attached to two different plants, maize and bean.The rate of photosynthesis in each leaf was measured at varying concentrations of carbon dioxide present in the intercellular spaces within the leaves. 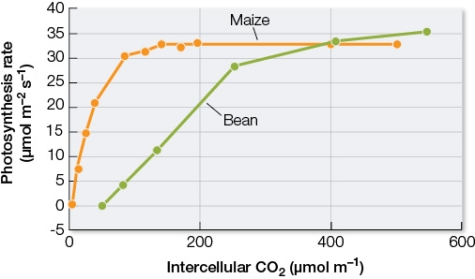 Based on these results, what is the likely classification of maize and bean plants, and which plant would grow better at reduced carbon dioxide levels?
Based on these results, what is the likely classification of maize and bean plants, and which plant would grow better at reduced carbon dioxide levels?
Definitions:
Systematic Random Sample
A sampling method where elements are selected from an ordered population using a fixed, periodic interval.
Random Selection
Random selection is a process in statistical sampling where each member of the population has an equal chance of being chosen, ensuring the sample is representative of the whole.
Sample
A sample is a subset of a larger population, selected for the purpose of analysis, which is used to infer or predict characteristics or outcomes for the whole population.
Statistic
A single measure, often derived from a sample, used to summarize or describe an aspect of the data.
Q41: Microtubules are formed between the poles and
Q52: Refer to the table.In Drosophila, white (w),
Q129: Refer to the graphs below. <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5650/.jpg"
Q141: Like glycolysis, fermentation occurs in the<br>A) mitochondria.<br>B)
Q142: Refer to the table below containing data
Q148: To study the mechanism of excitation in
Q162: In both photosynthesis and respiration, protons are
Q185: Refer to the figure showing nuclei of
Q233: As a result of fertilization, the number
Q254: Refer to the figure showing cyclin binding