Required:
Using the chart of accounts provided, indicate by account number the account or accounts that would be debited and credited in the following transactions. Also enter the number 1, 2, or 3 to indicate the type of transaction as: (1) an external transaction, (2) an internal transaction recorded as an adjusting journal entry, or (3) a closing entry. The company uses a perpetual inventory system. All prepayments are initially recorded in permanent accounts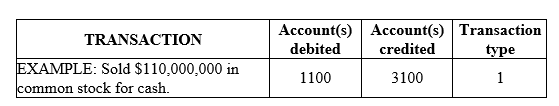
-Received payment for services to be performed next year.
Definitions:
Best Predictor
A variable or factor that most accurately forecasts or indicates a specific outcome.
Linear Effects
The impact on a dependent variable that is directly proportional to the change in an independent variable.
Coefficient
A constant or numerical value that precedes and multiplies the variable within an algebraic expression.
Neck
The narrow part connecting two larger parts or structures, such as the part of a bottle connecting its body to its opening or the part of the body that connects the head to the torso.
Q5: Prepare a classified balance sheet for China
Q7: The idea that tax cuts would increase
Q57: Tax revenue equals the size of the
Q67: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5911/.jpg" alt=" " class="answers-bank-image d-block" rel="preload"
Q87: Samson Inc. is contemplating the purchase of
Q88: Assume that at the time of signing
Q97: Popson Inc. incurred a material loss which
Q104: How does SFAC No. 157 define fair
Q120: Required: Compute the average collection period for
Q146: If a price floor is not binding,then