Figure 34-2
(a) The Money Market
(b) The Aggregate Demand Curve 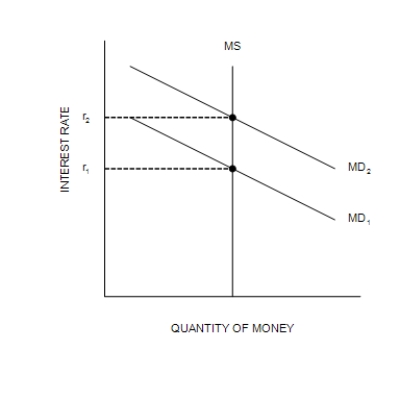
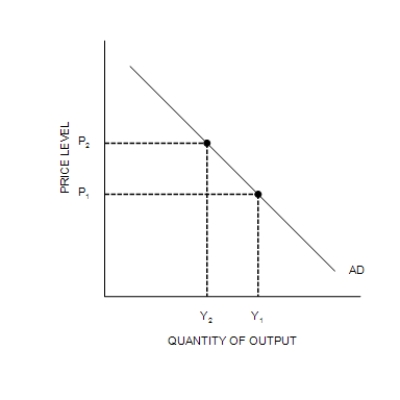
-Refer to Figure 34-2. A decrease in Y from Y1 to Y2 is explained as follows:
Definitions:
Commons Dilemma
A situation in social science illustrating problems of resource overuse in communities, where individual interests conflict with collective welfare.
Internal Locus
The belief that one has control over their life events and outcomes, as opposed to believing that external forces are responsible.
Dormitories
Living accommodations typically found in colleges or universities where students reside in shared rooms or halls.
AIDS
Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome, a chronic, life-threatening condition caused by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) that damages the immune system.
Q44: The short-run relationship between inflation and unemployment
Q50: The recession of 2008-2009 was preceded by<br>A)a
Q53: Refer to Figure 33-4.In the short run,a
Q62: According to the theory of liquidity preference,money
Q69: Refer to Figure 34-7.Which of the following
Q75: Supply-side economists believe that changes in government
Q77: When the dollar depreciates,U.S.<br>A)exports and imports increase.<br>B)exports
Q93: Changes in the interest rate bring the
Q105: In the long run,an increase in the
Q195: According to liquidity preference theory,equilibrium in the