Use the following to answer question:
Figure: The Profit-Maximizing Output and Price 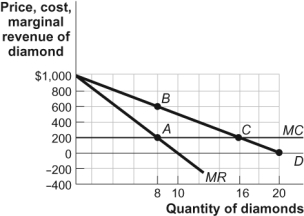
-(Figure: The Profit-Maximizing Output and Price) Use Figure: The Profit-Maximizing Output and Price.Assume that there are no fixed costs and AC = MC = $200.If this were a perfectly competitive industry,deadweight loss would be:
Definitions:
Equilibrium Output
The level of output where the aggregate supply equals aggregate demand, meaning there is no tendency for the economy to change size.
Short-Run Aggregate Supply
Shows the relationship between the price level and the quantity of goods and services that firms are willing and able to supply in the short term, holding some inputs fixed.
Long-Run Equilibrium
The price level and real GDP that occurs when (1) the actual price level equals the expected price level, (2) real GDP supplied equals potential output, and (3) real GDP supplied equals real GDP demanded.
Aggregate Demand Curve
Represents the total quantity of all goods and services that households, businesses, and government are willing to buy at each price level in an economy.
Q36: (Scenario: A Small-Town Monopolist)Use Scenario: A Small-Town
Q67: (Figure: Payoff Matrix for Ajinomoto and ADM)Use
Q71: (Figure: The Profit-Maximizing Firm in the Short
Q119: The market structure characterized by a few
Q128: An industry with a single producer that
Q142: Suppose a perfectly competitive industry is suddenly
Q173: When a monopoly maximizes profit,the loss of
Q173: The idea of diminishing returns to an
Q181: (Table: Variable Costs for Lawns)Use Table: Variable
Q286: A perfectly competitive industry is said to