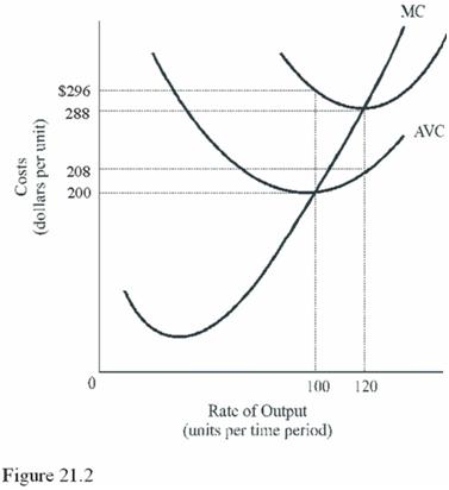
 In Figure 21.2, at what output does this firm maximize technical efficiency?
In Figure 21.2, at what output does this firm maximize technical efficiency?
Definitions:
Consumer Equilibrium
In marginal utility theory, the combination of goods purchased that maximizes total utility by applying the utility-maximizing rule. In indifference curve analysis, the combination of goods purchased that maximizes total utility by enabling the consumer to reach the highest indifference curve, given the consumer’s budget line (or budget constraint).
Prices
The amount of money required to purchase goods or services, often determined by supply and demand dynamics.
Utility-maximizing Combination
This refers to a situation where a consumer selects a combination of goods and services that provides the highest level of satisfaction or utility, given their budget constraint.
Marginal Utilities
The increased contentment or value obtained by a consumer through the consumption of one extra unit of a good or service.
Q7: When compared to a competitive market, monopolists
Q18: The demand for normal goods<br>A)Rises when incomes
Q64: A profit-maximizing monopolist produces the rate of
Q90: Suppose the quantity demanded of ski boats
Q97: The local baseball team owner hires you
Q101: A perfectly competitive firm has no market
Q118: The demand is more price-elastic<br>A)In the long
Q120: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5719/.jpg" alt=" The shaded area
Q125: Changes in short-run total costs result from
Q140: Accounting costs and economic costs differ because<br>A)Accounting