Suppose that the demand for a product depends on the price p according to 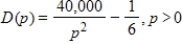 , where p is in dollars. Find and explain the meaning of the instantaneous rate of change of demand with respect to price when
, where p is in dollars. Find and explain the meaning of the instantaneous rate of change of demand with respect to price when 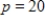 .
.
Definitions:
Significant Influence
The capacity, through investment ownership, to impact the management and policies of another company without having full control.
Net Income
The consummate earnings of a company following the subtraction of all operational costs and tax liabilities from its gross revenue.
Dividends
Payments made by a corporation to its shareholders, usually from profits.
Equity Method
An accounting technique used by companies to assess the profits earned by their investments in other companies, where the investment is recorded initially at cost and adjusted thereafter for the post-acquisition change in the investor's share of the investee's net assets.
Q1: The nurse is preparing a historical research
Q2: The nurse researcher is preparing information to
Q5: Find the derivative of the given function.
Q11: The nurse has participated in several research
Q14: What is the fifth term of the
Q40: Similar to the subject matter of Romanesque
Q54: What is the size of the payments
Q124: A frustrated store manager is asked to
Q162: Suppose that all license plates in a
Q209: Because the derivative of a function represents