Let 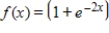 . Using a graphing utility, graph
. Using a graphing utility, graph 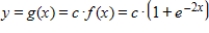 for
for 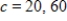 and
and 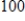 . What effect does c have on the graphs?
. What effect does c have on the graphs?
Definitions:
Pellicle
A flexible outer covering consisting of protein; characteristic of certain protists (e.g., ciliates and euglenoids).
Coralline
Referring to a type of algae that secretes calcium carbonate, contributing to the building of coral reefs.
Coral Reefs
Underwater ecosystems characterized by reef-building corals, which are colonies of tiny living animals found in marine waters containing few nutrients.
Pseudopodia
Temporary, amoeba-like projections of the cell surface which assist in the movement and feeding of some eukaryotic cells.
Q36: Use a table of the standard normal
Q44: The following table gives a city's unemployment
Q48: For the economy, what industry is most
Q53: A quiz consists of 10 multiple-choice questions
Q65: Graph the function. <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4005/.jpg" alt="Graph
Q78: Is the function <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4005/.jpg" alt="Is the
Q114: Write the transpose of matrix F.
Q115: As a result of a November 2004
Q143: In a certain city, the Democratic, Republican,
Q182: The graphs of a company's total revenue