Set up the system of equations and then solve it by using inverse matrices.
Bee ancestry Because a female bee comes from a fertilized egg and a male bee comes from an unfertilized egg, the number  of ancestors of a male t + 2 bee generations before the present generation is the sum of the number of ancestors t and t + 1 generations
of ancestors of a male t + 2 bee generations before the present generation is the sum of the number of ancestors t and t + 1 generations 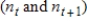 before the present. If the numbers of ancestors of a male bee in a given generation t and in the previous generation are given by
before the present. If the numbers of ancestors of a male bee in a given generation t and in the previous generation are given by 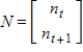 , then there is a matrix M such that the numbers of ancestors in the two generations preceding generation t are given by
, then there is a matrix M such that the numbers of ancestors in the two generations preceding generation t are given by 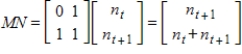 .
.
For a given male bee, the numbers of ancestors 5 and 6 generations back are given by  .
.
Find the numbers of ancestors 4 and 5 generations back by multiplying both sides of 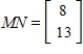 by the inverse of M.
by the inverse of M.
Definitions:
Sustainable Growth Rate
The maximum rate at which a company can grow its revenues and profits without needing to increase financial leverage.
Debt-Equity Ratio
An indicator of a firm's use of financial debt, found by dividing the total amount of liabilities by the equity owned by stockholders.
Retention Ratio
The proportion of net income that is retained in the company rather than paid out to shareholders as dividends.
Growth Rate
A measure of the increase in size, number, value, or strength of a business or other entity's key metric over a specified period of time.
Q4: Suppose the Cobb-Douglas production function for a
Q8: If <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4005/.jpg" alt="If find
Q18: The following table gives the percent of
Q40: The concentration y of a certain drug
Q45: A simplex matrix is given. In this
Q74: Suppose the economy of an underdeveloped country
Q86: Sketch the graph of the function <img
Q106: The following table gives the percent of
Q112: A chemical storage tank has a capacity
Q114: A house is rented for $3,700 per