A planar electromagnetic wave is propagating in the +x direction. At a certain point P and at a given instant, the electric field of the wave is given by 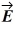 = (0.082 V/m) ĵ. What is the Poynting vector at the point P at that instant? (c = 3.0 x 108 m/s, μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A, ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
= (0.082 V/m) ĵ. What is the Poynting vector at the point P at that instant? (c = 3.0 x 108 m/s, μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A, ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
Definitions:
Cobb-Douglas Production Function
The Cobb-Douglas Production Function is an economic model representing the relationship of an output to inputs, typically showing how labor and capital contribute to the production process in a way that reflects diminishing returns.
Returns to Scale
The rate at which output increases as inputs are increased proportionally in the production process.
Logarithmic Variable Cost Function
A formula representing the variable costs of production as a logarithmic function, indicating how these costs evolve as production volume changes.
Increasing Rate
Often refers to a situation where the rate of change of a variable is accelerating; a concept applicable in various economic, financial, and mathematical contexts.
Q2: One fairly crude method of determining the
Q10: Estimate the rotational energy (in eV) for
Q20: A thin converging lens is found to
Q22: Which one of the following lists is
Q23: An LC circuit consists of a 3.4-µF
Q26: As shown in the figure, a small
Q36: A galvanometer has an internal resistance of
Q43: A 6.00-μF parallel-plate capacitor has charges of
Q43: The emf and the internal resistance of
Q58: A fish appears to be 2.00 m