The stability of 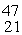 Sc with respect to alpha, β+, and β- decay is to be determined. Do not consider the possibility of decay by electron capture. The following atomic masses are known:
Sc with respect to alpha, β+, and β- decay is to be determined. Do not consider the possibility of decay by electron capture. The following atomic masses are known: 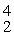
He: 4.002603 u 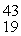
K: 42.960717 u 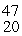
Ca: 46.954543 u 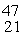
Sc 46.952409 u 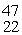
Ti: 46.951764 u
The 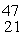
Sc nuclide is
Definitions:
Models
Models are simplified representations or frameworks used to explain complex systems or processes, aiding in understanding and prediction.
Retention Strategies
Are approaches undertaken by organizations to keep employees and reduce turnover rates.
Job Dissatisfaction
A negative emotion towards one’s job due to various factors like working conditions, relationships, or a mismatch between job expectations and reality.
Causes
The reason or motive for an action or condition, leading to a certain outcome or effect.
Q1: What type of particle is an electron?
Q2: A major reason that Hispanic Americans had
Q8: According to Shakespeare, bereaved persons need to<br>A)
Q11: Neimeyer describes "meaning reconstruction" by bereaved persons
Q13: Changes in American death rates can be
Q24: How many electrons does it take to
Q29: Attitudes are defined as<br>A) ways of presenting
Q37: Projected average life expectancy for all individuals
Q38: Acts of terrorism in the 21<sup>st</sup> century<br>A)
Q40: For the missing product X in the