A stationary plutonium-239 nucleus decays into a uranium-235 nucleus plus an alpha particle. The energy released in the process is 5.24 MeV. Given the following mass values 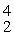 He: 4.002603 u
He: 4.002603 u 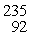
U: 235.043924 u
What is the kinetic energy of the 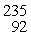
U nucleus? (1 u =931.494 MeV/c2)
Definitions:
Wavelength
The distance between successive crests of a wave, especially points in a sound wave or electromagnetic wave.
Sense of Color
is the capacity to perceive and distinguish between different colors, including their hues, saturation, and brightness, primarily mediated by the cone cells in the human eye.
Iris
The colored part of the eye that controls the size of the pupil and the amount of light that enters the eye.
Refraction
The bending of light as it passes from one medium to another with a different density, affecting its speed and direction.
Q5: A diatomic molecule has 18 × 10<sup>-5</sup>
Q12: According to Kastenbaum, a "death system"<br>A) includes
Q17: A vibrating diatomic molecule has vibrational quantum
Q20: If the accuracy in measuring the position
Q25: Death education needs to develop special sensitivity
Q30: Estimate the speed of a galaxy away
Q32: Upon being struck by 240-nm photons, a
Q34: The Puritans of 17<sup>th</sup> century New England
Q58: In massive stars, three helium nuclei fuse
Q72: Which of the following descriptions best describes