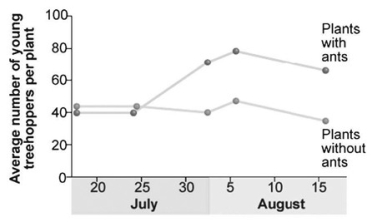
 Treehoppers (a type of insect) produce honeydew, which ants use for food. Treehoppers have a major predator, the jumping spider. Researchers hypothesized that the ants would protect the treehoppers from the spiders. In an experiment, researchers followed study plots with ants removed from the system and compared them to a control plot. In the figure shown, what can you conclude?
Treehoppers (a type of insect) produce honeydew, which ants use for food. Treehoppers have a major predator, the jumping spider. Researchers hypothesized that the ants would protect the treehoppers from the spiders. In an experiment, researchers followed study plots with ants removed from the system and compared them to a control plot. In the figure shown, what can you conclude?
Definitions:
Hippocampus
A region of the brain associated with memory formation and spatial navigation, critical in converting short-term memories to long-term.
Memory Errors
Mistakes or distortions in the recall of information or experiences, often due to the limitations or failures in the human memory system.
Sexual Assault
Any sexual activity or behavior that occurs without the explicit consent of the recipient.
Hypnotizes
The act of inducing a trance-like state in which a person is more open to suggestion, typically for therapeutic purposes.
Q2: You have discovered an enzyme that can
Q6: Which of the following is a TRUE
Q9: A 3-hectare lake in the American Midwest
Q11: Based on the data in the accompanying
Q13: Bacteria, insects, and plants use carbohydrates to
Q14: Use the accompanying figure to answer this
Q22: Which island would likely exhibit the most
Q41: The regulation of blood sugar levels and
Q51: Which of the following statements regarding the
Q54: Her immune system's recognition of the second