The next questions refer to the following table, which compares the % sequence homology of four different parts (two introns and two exons) of a gene that is found in five different eukaryotic species. Each part is numbered to indicate its distance from the promoter (e.g., Intron I is the one closest to the promoter) . The data reported for species A were obtained by comparing DNA from one member of species A to another member of species A.
% Sequence Homology
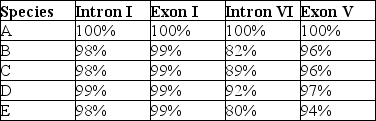
-Regarding these sequence homology data, the principle of maximum parsimony would be applicable in
Definitions:
Social Role Disorientation
Confusion or uncertainty about social roles due to changing societal expectations or personal transitions.
Durkheim's Theory
A sociological perspective proposed by Emile Durkheim that studies how societal forces and structures influence behavior, norms, and values.
Anomic Suicide
Suicide committed by people who experience a severe disorientation and role confusion because of a large change in their relationship to society.
Suicidal
Pertains to having thoughts, tendencies, or behaviors associated with taking one's own life.
Q3: To make a vaccine against mumps, measles,
Q20: Which of the following viruses would most
Q26: When many genes of an organism are
Q28: Gastrulation is an important event in early
Q29: When a mosquito infected with Plasmodium first
Q30: Which of the following are maternal effect
Q32: What is the major difference between Bromus
Q42: The B-I mutation in anthocyanin (red pigments)
Q47: Which of the following involves an increase
Q56: Upon being formed, oceanic islands, such as