Use the following to answer questions
Scenario I
Scenario I is based on and provides fabricated data consistent with the following study:
Barber,S.J. ,Rajaram,S. ,& Fox,E.B.(2012) .Learning and remembering with others: The key role of retrieval in shaping group recall and collective memory.Social Cognition,30(1) ,121-132.doi:10.1521/soco.2012.30.1.121
In a typical experiment on collaborative memory,participants first encode information individually and later attempt to recall the information either individually or in a small group (collaboratively) .While the recall of the collaborative group is better than that of any individual,the summed recall of individuals typically is better than the recall of the collaborative group.This is a phenomenon termed collaborative inhibition.Barber,Rajaram,and Fox (2012) investigated this phenomenon during both the encoding and retrieval stages of memory.
Participants created sentences out of a word bank,which provided for the opportunity to encode this information.After completing this task,participants engaged in an unrelated task-solving mazes-for 10 minutes.Then,in a surprise memory test,they were asked to recall as many words from the word bank as possible (retrieval) .
Participants were randomly assigned to one of four groups.In the first group (Alone-Alone) ,participants were studied individually during both the encoding and retrieval phases of the experiment.In the second group (Alone-Collaborative) ,participants were studied individually during the encoding phase and studied as part of a three-member team (triad) during the retrieval phase.In the third group (Collaborative-Alone) ,participants were studied in a triad during the encoding phase but individually during the retrieval phase.Finally,in the fourth group (Collaborative-Collaborative) ,participants completed both phases of the experiment as part of a triad.
Fabricated results illustrating the major finding of Barber et al.(2012) are presented in Figure 6.1.This figure shows the percentage of words from the word bank accurately recalled as a function of group.For the two groups that experienced the retrieval phase individually,scores represent the summed retrieval of the individuals comprising the group.For the two groups that experienced the retrieval phase as part of a triad,scores simply represent the collaborative performance.
Figure 6.1 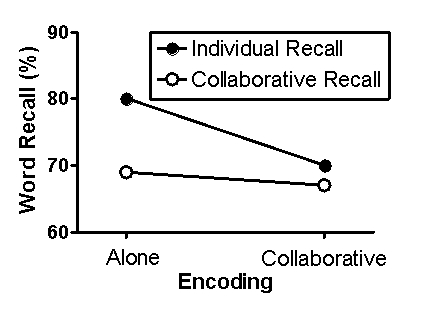
-(Scenario I) If interested only in the effects of individual or collaborative encoding on subsequent retrieval,one should examine the:
Definitions:
Computer-Mediated Communication
The exchange of messages between two or more people through digital media, such as email, messaging apps, and social networks.
Codability
The ease with which information can be encoded, stored, and recalled in memory, often influenced by the organization and familiarity of the information.
Non-Verbal Channels
Methods of communication that do not involve words, such as body language, gestures, facial expressions, and tone of voice.
Asynchronous
Referring to events that do not occur at the same time or processes that do not operate simultaneously, often used in the context of communication where responses can occur at any time.
Q12: In Pavlov's research,what was the CR?<br>A)pricking ears
Q17: Distributed practice is better than massed practice
Q43: Rachel was asked the following questions: "What
Q68: Mind wandering is especially likely when we
Q93: The radio DJ says,"Sometime this hour,I'll be
Q94: Which term in the three-term contingency refers
Q113: Short-term memory is to working memory as:<br>A)structure
Q213: Which factor is causally related to deciding
Q257: Jeremy goes to crowded parties and approaches
Q292: Callie visited a dance club where the