Scenario II
The following scenario presents fabricated data consistent with the results of the following study:
Tienari, P., Wynne, L. C., Sorri, A., Lahti, I., Läksy, K., Moring, J., & ... Wahlberg, K. (2004) . Genotype-environment interaction in schizophrenia-spectrum disorder: Long-term follow-up study of Finnish adoptees. The British Journal of Psychiatry, 184(3) , 216-222. doi:10.1192/bjp.184.3.216
Schizophrenia affects approximately 1 percent of the general population and is characterized by the profound disruption of basic psychological processes; a distorted perception of reality;, altered or blunted emotional affect; and disturbances in thought, motivation, and behavior. The symptoms of schizophrenia are varied and are typically classified as either positive or negative. Positive symptoms of schizophrenia refer to thoughts and behaviors typically not observed in those without the disease, and can include things like delusions (patently false beliefs) , hallucinations (false perceptual experiences) , and disorganized speech. Negative symptoms of schizophrenia are deficits or disruptions in normal behaviors, such as social withdrawal. Cognitive deficits in executive functioning, attention span, and working memory also may be observed.
The symptoms of schizophrenia usually begin in late adolescence and the disease has a strong genetic component. Over the years, a number of biological factors have been linked to schizophrenia, although none alone adequately accounts for the disorder. One such example is the dopamine hypothesis, which states that schizophrenia is related to an excess in dopamine activity. Another theory points to enlarged brain ventricles and progressive cortex tissue loss as predictive of schizophrenia, although only a minority of persons with schizophrenia have enlarged ventricles, this structural anomaly can appear in those without the disease, and dopamine antagonists also may produce this effect.
Although research into the environmental determinants of schizophrenia has focused largely on the prenatal environment, psychological and social factors also contribute. Tienari et al. (2004) compared the risk of developing schizophrenia in children adopted into healthy versus disturbed families, the latter characterized by extreme conflict, volatile relationships, and communication deficits. Some of these children under investigation were identified as at-risk genetically for schizophrenia because their biological mothers were schizophrenic. The remainder was classified at low risk. The investigators utilized a longitudinal design and obtained the diagnostic status of the children with respect to schizophrenia when they reached young adulthood. Fabricated results consistent with this study are shown in Figure 15.2
Figure 15.2 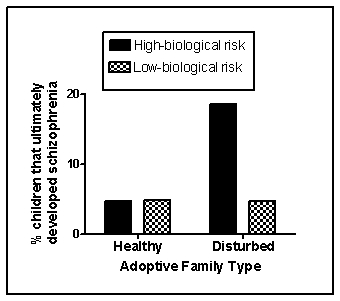
-(Scenario II) The results shown in Figure 15.2 demonstrate that:
Definitions:
Contingency Factors
External and internal conditions that influence the effectiveness of management strategies and determine the success of certain managerial actions.
Motivational Practice
Techniques or strategies used to inspire or encourage individuals or groups to achieve their goals or improve their performance.
Organization Characteristics
The features and attributes that define an organization's structure, culture, and processes.
Motivational Practices
Strategies or methods applied to encourage and increase motivation among individuals or groups.
Q7: The _ is the classification system of
Q10: During a fight-or-flight response, the adrenal glands
Q20: Jill has an abrasion on the cornea
Q25: Married people have a lower risk of
Q44: Psychotherapy has a risk of being harmful.
Q52: Which statement regarding mobile health interventions is
Q73: Which therapy assumes everyone has a tendency
Q73: The heritability estimate for major depression averages
Q111: Jose is terrified that someone is going
Q131: Why are antidepressants not prescribed to treat