Scenario I
Scenario I is based on and presents results consistent with the following studies:
Snedeker, J., Geren, J., & Shafto, C. L. (2012) . Disentangling the effects of cognitive development and linguistic expertise: A longitudinal study of the acquisition of English in internationally-adopted children. Cognitive Psychology, 65(1) , 39-76. doi:10.1016/j.cogpsych.2012.01.004
Snedeker, J., Geren, J., & Shafto, C. L. (2007) . Starting over: International adoption as a natural experiment in language development. Psychological Science, 18(1) , 79-87. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9280.2007.01852.x
Language development occurs in orderly stages, beginning with one-word utterances and progressing to two-word utterances, simple sentences containing function morphemes, and the emergence of grammatical rules. Psycholinguists have attempted to determine if language development is a consequence of cognitive development or if it reflects linguistic processes that occur independently of general cognitive development. Studies on the acquisition of a second language in internationally adopted children have provided insight into this research question. In a series of studies, Snedeker et al. (2007, 2012) studied the acquisition of the English language in adopted preschoolers from China. These children had no exposure to the English language before being adopted by families in the United States.
Figure 9.1 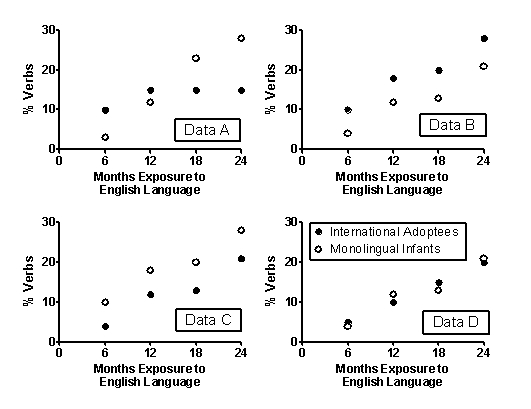
-(Scenario I) Snedeker et al. (2007) studied the acquisition of English as a second language in preschool children adopted from China. In trying to disentangle the role of linguistic and cognitive development on language acquisition, which of these would serve as the most appropriate control group?
Definitions:
Phototropin
A protein that acts as a blue-light receptor, causing phototropic responses in plants towards light sources.
Phototropic Response
the growth or movement of a plant organ toward or away from light, as a response to its direction.
Phytochrome
A blue-green, proteinaceous pigment involved in a wide variety of physiological responses to light; occurs in two interconvertible forms, Pr (red-absorbing phytochrome) and Pfr (far-red-absorbing phytochrome).
Bolting
The production of a tall flower stalk by a plant that grows vegetatively as a rosette (growth habit with a short stem and a circular cluster of leaves).
Q6: Asian and African cultures are more likely
Q7: Monozygotic twins share _ percent of their
Q17: The first intelligence tests were developed as
Q32: People with Capgras syndrome suffer from amnesia
Q38: Algorithms are mental shortcuts that sometimes lead
Q89: Brandon is unable to identify animals, such
Q108: The heritability coefficient of intelligence is roughly:<br>A).5.<br>B).6.<br>C).7.<br>D).8.
Q110: The hedonic principle refers to the view
Q110: The best, or most typical, member of
Q132: Cross-cultural research on preliterate societies suggest that