Scenario II
Scenario II is based on and presents fabricated data consistent with the following study:
MacDonald, S., Uesiliana, K., & Hayne, H. (2000) . Cross-cultural and gender differences in childhood amnesia. Memory, 8(6) , 365-376. doi:10.1080/09658210050156822
MacDonald and colleagues (2000) investigated cultural and gender influences on the age and quality of first childhood memories. Specifically, they interviewed males and females from three cultures-Asian, Pakeha, and Maori-and asked them to describe their earliest childhood memory in as much detail as possible. The researchers recorded the age of the earliest memory and also quantified the total amount of information given in the memory description. Figure 1.2A shows the number of participants reporting their first memory as a function of age not separated by gender or culture. Figure 1.2B shows the mean age of the first memory as a function of gender and culture, and Figure 1.2C shows the mean total information present in that memory as a function of gender and culture.
Figure 1.2A (left) , Figure 1.2B (middle) , and 1.2C (right) 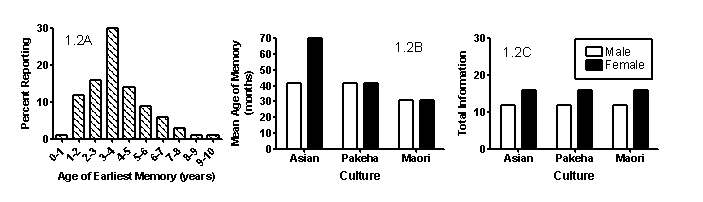
-(Scenario II) Someone who reads this study and concludes that females have more accurate childhood memories than males is:
Definitions:
Economic Profit
The difference between total revenue and total costs, including both explicit and implicit costs, representing the financial gain in excess of the opportunity costs of resources used.
X-Inefficiency
The difference between efficient behavior of enterprises assumed or implied by economic theory and their observed behavior in practice, often due to a lack of competitive pressure.
Pure Competition
A market structure characterized by many small firms producing identical products, where no single firm has significant control over the market price.
Monopolistic Competition
A market structure characterized by many producers selling products that are similar but not identical, allowing for competition based on quality, price, and brand.
Q2: Kyle has seen his father hit his
Q6: Supplementing the incomes of poor families to
Q12: In order for a study to be
Q15: Given the marriage universals and distinctions around
Q22: Discuss the four conditions that influence the
Q37: A positive correlation between smoking and mental
Q64: The term "patient" is to psychoanalysis as
Q86: Important frauds are more likely to be
Q98: Which mental health professionals assist people in
Q121: "The goal of scientific psychology should be