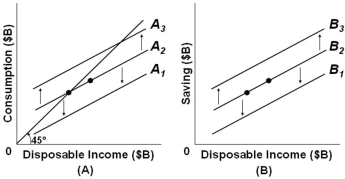
 Refer to the above figures with consumption schedules in figure (A) and saving schedules in figure (B) , which correspond to each other across different levels of disposable income. If, in figure (A) , line A2 shifts to A3 because of the so-called wealth effect, then in figure (B) line:
Refer to the above figures with consumption schedules in figure (A) and saving schedules in figure (B) , which correspond to each other across different levels of disposable income. If, in figure (A) , line A2 shifts to A3 because of the so-called wealth effect, then in figure (B) line:
Definitions:
Specific Causes
Unique factors or circumstances that can lead to specific outcomes or effects, distinguished from general or common causes.
Acceptance Sampling
A statistical quality control method where a random sample of items from a lot is inspected to decide if the whole lot should be accepted or rejected.
Defective Items
Products that fail to meet quality standards or specifications, often resulting in returns or waste.
AOQ
Average Outgoing Quality, a measure in quality control that represents the average quality level of products leaving the manufacturing process.
Q4: The following are important problems associated with
Q24: The immediate-short-run aggregate supply curve is:<br>A) Vertical<br>B)
Q40: Gross domestic private investment, as defined in
Q90: Assume that an increase in a household's
Q93: Proponents of zero inflation argue that even
Q93: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4895/.jpg" alt=" Refer to the
Q102: A Federal budget deficit exists when:<br>A) Federal
Q104: Consumption is $141 billion, planned investment is
Q114: Which of the following is best considered
Q138: The crowding-out effect works through interest rates