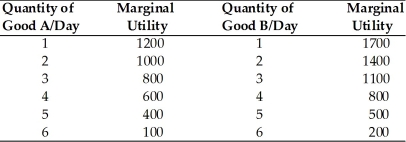
-Refer to the above table. If the price of Good A is $1, the price of Good B is $2, and the consumer has $13, the rational consumer will purchase
Definitions:
Producer Surplus
The difference between what producers are willing to accept for a good versus what they actually receive, typically represented by an area on a graph.
Supply Curve
A graph displaying the relationship between the price of a good or service and the quantity of that good or service that a supplier is willing and able to provide, holding all else equal.
Diminishing Marginal Product
A principle stating that as more of a variable input is added to a fixed input, the additional output produced from each additional unit of the variable input eventually decreases.
Marginal Costs
The supplementary cost arising from the manufacture of an extra unit of a good or service.
Q19: The quantity of good A is measured
Q22: For any two goods, A and B,
Q146: The analysis of consumer decision making based
Q208: The greatest advantage of a corporation is<br>A)
Q261: A movement along the production possibilities curve
Q274: An indifference curve shows<br>A) the combinations of
Q290: Which of the following will most likely
Q389: In cardinal utility analysis<br>A) numbers can be
Q414: Present value is<br>A) the value of a
Q420: A firm is considering three projects. Each