Kenrick Corporation uses activity-based costing to compute product margins.In the first stage, the activity-based costing system allocates two overhead accounts-equipment expense and indirect labor-to three activity cost pools-Processing, Supervising, and Other-based on resource consumption.Data to perform these allocations appear below: 
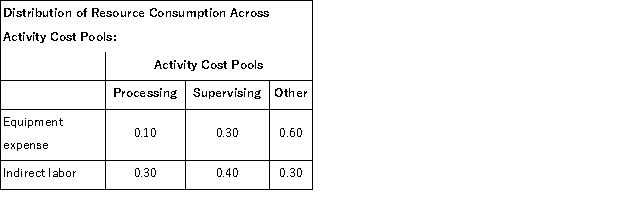 In the second stage, Processing costs are assigned to products using machine-hours (MHs) and Supervising costs are assigned to products using the number of batches.The costs in the Other activity cost pool are not assigned to products.Activity data for the company's two products follow:
In the second stage, Processing costs are assigned to products using machine-hours (MHs) and Supervising costs are assigned to products using the number of batches.The costs in the Other activity cost pool are not assigned to products.Activity data for the company's two products follow: 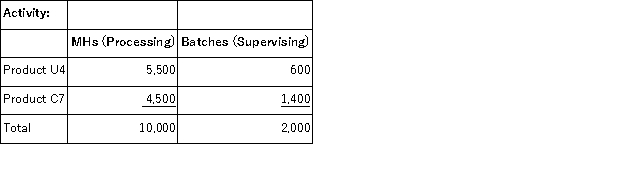 Finally, sales and direct cost data are combined with Processing and Supervising costs to determine product margins.
Finally, sales and direct cost data are combined with Processing and Supervising costs to determine product margins. 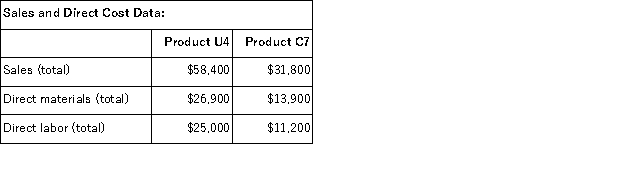 The activity rate for the Processing activity cost pool under activity-based costing is closest to:
The activity rate for the Processing activity cost pool under activity-based costing is closest to:
Definitions:
Long-term Liability
A long-term liability is a financial obligation of a company that is due beyond one year, such as bonds payable, long-term leases, and pension obligations.
Capital Lease Obligations
Long-term lease agreements that are recorded as assets on a company's balance sheet, effectively treating the lease as a purchase of the asset.
Current Portion
The portion of long-term liabilities that is due to be paid within the next twelve months.
Operating Lease
A leasing agreement that allows for the use of an asset but does not convey rights of ownership, often treated as an operational expense rather than a capital expense.
Q35: When closing overapplied manufacturing overhead to cost
Q93: Mussenden Corporation has an activity-based costing system
Q107: Chown Corporation, which has only one product,
Q134: In activity-based costing, organization-sustaining costs should be
Q139: Hadley Inc. , makes a line of
Q159: Dockwiller Inc.manufactures industrial components.One of its products,
Q170: Eliminating nonproductive processing time is particularly important
Q172: Brees Inc. , a company that produces
Q173: Hermenegildo Corporation is presently making part P42
Q202: Delvin Corporation, which has only one product,