Consider the following calculations for a one-way analysis of variance from a completely randomized design with 20 total observations.The response variable is sales in millions of dollars and four treatment levels represent the four regions that the company serves. MSE = 101.25 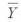 overall = 39
overall = 39 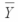 1 = 33
1 = 33 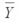 2 = 43
2 = 43 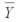 3 = 49
3 = 49 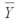 4 = 31
4 = 31
Perform a pairwise comparison between treatment mean 1 and treatment mean 4 by computing a Tukey 95% simultaneous confidence interval.
Definitions:
Two-dimensional Table
A data structure that arranges information in rows and columns, effectively forming a grid.
GridLayout
A layout manager in Java Swing that arranges components in a rectangular grid.
Menu Item
A component in graphical user interfaces that represents an option or command in a menu.
JMenuItem
JMenuItem is a component of the Java Swing library used to implement items in a menu.
Q20: The sampling distribution of <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1737/.jpg" alt="The
Q22: In one-way ANOVA,the numerator degrees of freedom
Q37: The range of feasible values for the
Q81: Last year,KAAA's share of the 6
Q82: At a recent meeting of educational researchers,comparisons
Q94: Parameters of the F distribution include:<br>A)n<sub>1</sub><br>B)degrees of
Q103: When comparing the variances of two normally
Q115: The manufacturer of a light fixture believes
Q123: A sample of 400 journalism majors at
Q136: When the level of confidence and sample