Use the following diagram to answer the next problem. 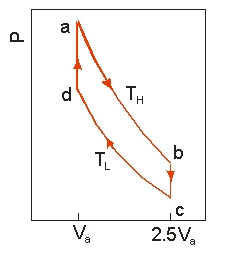 An ideal heat engine uses 0.01 mol of gas and operates between a hot reservoir at
An ideal heat engine uses 0.01 mol of gas and operates between a hot reservoir at
TH = 400 K and cold reservoir at TL = 300 K, in a cycle from a→b→c→d→a. From a→b the gas undergoes an isothermal expansion, changing its volume from Va to 2.5Va. From b→c, the pressure is reduced at a constant volume. From c→d, the gas undergoes an isothermal compression, and from d→a, the pressure is increased at a constant volume until the gas is back at the original condition at a.
-How much work is obtained from the engine in each cycle?
Definitions:
Activity Rate
An activity rate is the cost driver rate used in activity-based costing to allocate overhead costs to products or services.
Activity-based Costing
An accounting method that assigns costs to products or services based on the activities and resources that go into their production, providing more accurate cost information.
Resource Consumption
The use of resources (such as raw materials, energy, or labor) by a process, project, or activity, typically measured to manage efficiency and costs.
Activity-based Costing
A costing methodology that assigns costs to products or services based on the resources they consume.
Q6: A particle moving in a circle of
Q13: The length of an object varies with
Q18: If the rms speed of oxygen molecules
Q22: A capacitor of capacitance C holds a
Q28: An ideal monatomic gas has a molar
Q40: In a certain particle accelerator,a current
Q44: Three charges are located at 100-m
Q45: The work required to move a third
Q77: Calculate the point on the Fahrenheit scale
Q115: What is the amplitude after 1 s?<br>A)2