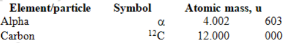
After a star fuses most its hydrogen into helium, it begins to fuse the helium into carbon. The energy released in fusing helium nuclei ( particles) into carbon is approximately
Definitions:
Systematic Risk
The inherent risk associated with the entire market or market segment, also known as market risk.
Beta Coefficient
A means of gauging the rate of fluctuation, or uniform risk, inherent in a security or portfolio as compared to the entire market.
Treynor Index
A performance metric for determining how well an investment portfolio is compensated for taking investment risk, adjusted for market volatility.
Unsystematic Risk
The risk associated with a specific issuer of a security, such as a company's financial health or management decisions, also known as "specific risk" or "idiosyncratic risk."
Q4: Since auditing is a public profession, auditors
Q8: In considering the effectiveness of evidence gathering
Q16: The two oxygen atoms in the O<sub>2</sub>
Q25: Under which of the following circumstances would
Q26: Initially a mixture of two radioactive sources
Q37: The internal control objective of accuracy is
Q37: A value-for-money (VFM) audit will tend to
Q108: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6081/.jpg" alt=" The portion of
Q119: The Pauli exclusion principle states that
Q127: The volume of a nucleus is directly