In the diagram below, use the base-pairing rules for DNA and RNA to label the strand of RNA (right) that is complementary to the single strand of DNA (left), where C = cytosine, G = guanine, A = adenine, T = thymine, and U = uracil. Then circle and label an example of a nucleotide and a nucleoside, showing the double-stranded DNA and RNA hybrid. Based on the orientation of the sugar molecules, label the four ends of the molecule as 3´ or 5´? showing the double-stranded DNA and RNA hybrid. 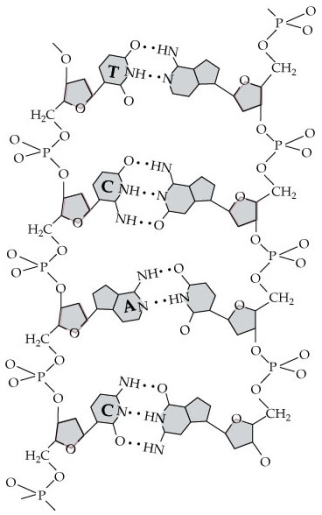
Definitions:
Government Subsidy
Financial assistance provided by the government to businesses, individuals, or other governmental units in support of an activity deemed beneficial to the public.
Supply
The total amount of a product or service that is available to consumers, determined by factors such as price, production costs, and market demand.
Allocative Efficiency
A state of the market where resources are allocated in a way that maximizes the net benefit to society, ensuring that every good or service is produced up to the point where the last unit provides a benefit equal to its cost of production.
Productive Efficiency
A situation where the economy or a production process is unable to produce more of one good without reducing the production of another good, using available resources in the best way.
Q7: The hormone responsible for flowering in some
Q23: Plants that concentrate the harmless amino acid
Q32: Which of the following is not an
Q48: HIV can be transmitted from person to
Q52: Steroid hormones<br>A) are produced only by the
Q68: In DNA, A pairs with T, and
Q77: Virally infected cells often produce small amounts
Q81: Explain what is meant by coevolution of
Q127: Grazed plants may exhibit increased productivity because
Q144: Also known as antigenic determinants, _ are