Velocities have both direction and magnitude and thus are vectors. The magnitude of a velocity vector is called speed. Suppose that a wind is blowing from the direction N 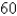
 W at a speed of
W at a speed of 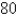 km/h. (This means that the direction from which the wind blows is
km/h. (This means that the direction from which the wind blows is 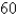
 west of the northerly direction.) A pilot is steering a plane in the direction N
west of the northerly direction.) A pilot is steering a plane in the direction N 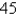
 E at an airspeed (speed in still air) of
E at an airspeed (speed in still air) of 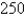 km/h. The true course, or track, of the plane is the direction of the resultant of the velocity vectors of the plane and the wind. The ground speed of the plane is the magnitude of the resultant. Find the ground speed of the plane. Round the result to the nearest hundredth.
km/h. The true course, or track, of the plane is the direction of the resultant of the velocity vectors of the plane and the wind. The ground speed of the plane is the magnitude of the resultant. Find the ground speed of the plane. Round the result to the nearest hundredth.
Definitions:
Q8: Find parametric equations for the tangent line
Q14: Find the area of the surface. The
Q18: Determine whether the series converges or diverges.
Q22: Find the center of mass of the
Q24: Find an equation of the hyperbola centered
Q34: Find the exact area of the surface.
Q61: Find the radius of convergence and the
Q71: A sequenceis <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5971/.jpg" alt="A sequenceis
Q76: A cardboard box without a lid is
Q96: Find equations for the tangent plane and