In the LORAN (LOng RAnge Navigation) radio navigation system, two radio stations located at A and B transmit simultaneous signals to a ship or an aircraft located at P. The onboard computer converts the time difference in receiving these signals into a distance difference 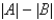 , and this, according to the definition of a hyperbola, locates the ship or aircraft on one branch of a hyperbola (see the figure) . Suppose that station B is located L =
, and this, according to the definition of a hyperbola, locates the ship or aircraft on one branch of a hyperbola (see the figure) . Suppose that station B is located L = 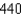 mi due east of station A on a coastline. A ship received the signal from B
mi due east of station A on a coastline. A ship received the signal from B 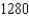 microseconds (µs) before it received the signal from A. Assuming that radio signals travel at a speed of
microseconds (µs) before it received the signal from A. Assuming that radio signals travel at a speed of 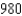 ft /µs and if the ship is due north of B, how far off the coastline is the ship? Round your answer to the nearest mile.
ft /µs and if the ship is due north of B, how far off the coastline is the ship? Round your answer to the nearest mile. 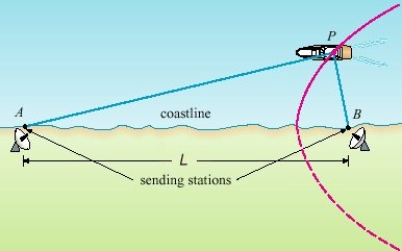
Definitions:
Dilutive Potential
The possibility that the issuance of additional securities could decrease earnings per share or decrease an ownership interest.
After-tax Effect
The impact of taxes on a company's financial transactions, typically focusing on the net result after accounting for the taxation impact.
Accounting Policies
The distinct protocols, core principles, guidelines, directives, and procedures followed by a company for the preparation and presentation of its financial reports.
Retrospective Adjustment
An adjustment applied to the financial statements of prior periods to correct an error or to reflect a change in accounting policy as if that policy had always been applied.
Q3: Find the surface area generated by rotating
Q4: Suppose (1, 1) is a critical point
Q23: Solve the differential equation. <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5971/.jpg" alt="Solve
Q32: Biologists stocked a lake with <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5971/.jpg"
Q44: Let c be a positive number. A
Q48: Determine the number of terms sufficient to
Q49: Find the shortest distance from the point
Q84: Find the length of the line segment
Q103: Use the definition of partial derivatives as
Q132: The temperature-humidity index I (or humidex, for