The marginal cost function 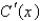 is defined to be the derivative of the cost function. If the marginal cost of manufacturing x units of a product is
is defined to be the derivative of the cost function. If the marginal cost of manufacturing x units of a product is 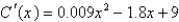 (measured in dollars per unit) and the fixed start-up cost is
(measured in dollars per unit) and the fixed start-up cost is 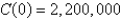 , use the Total Change Theorem to find the cost of producing the first 5,000 units.
, use the Total Change Theorem to find the cost of producing the first 5,000 units.
Definitions:
Placebo Effect
The beneficial effect on a patient's health condition following a placebo treatment, due to the patient's belief in the treatment's efficacy.
Sampling Bias
A systematic error in a research study resulting from non-random sampling of participants, leading to unrepresentative sample data.
Experimenter Bias
A type of bias that occurs when a researcher's expectations or preferences about the outcome of a study influence the results obtained.
Socially Desirable Responding
The tendency of respondents to answer questions in a manner that will be viewed favorably by others, often leading to overreporting of "good" behavior and underreporting of "bad" behavior.
Q35: The Pacific halibut fishery has been modeled
Q45: Find the area that the curve encloses.
Q57: Determine whether the series is convergent or
Q65: Determine whether the improper integral converges or
Q72: Determine the largest set on which the
Q79: Write the expression in algebraic form.<br>sec(sin<sup>-</sup><sup>1</sup> 8x)
Q82: Find the centroid of the region bounded
Q91: The acceleration function (in m / s<sup>2</sup>)
Q143: Find the radius of convergence and the
Q146: Use the sum of the first 9