When we test H0: μ1 − μ2 £ 0,HA: μ1 − μ2 > 0, 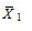 = 15.4,
= 15.4, 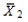 = 14.5,s1 = 2,s2 = 2.28,n1 = 35,and n2 = 18 at α = .01,can we reject the null hypothesis? (Assume unequal variances. )
= 14.5,s1 = 2,s2 = 2.28,n1 = 35,and n2 = 18 at α = .01,can we reject the null hypothesis? (Assume unequal variances. )
Definitions:
Demand Curve
This depicts how consumer demand for a product changes as the price of that product changes, illustrating the inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded.
Perfectly Elastic
Describes a situation in which quantity demanded or supplied changes infinitely in response to any change in price, visualized as a horizontal line on a demand or supply graph.
Marginal Revenue Curve
A graphical representation showing how marginal revenue varies as the quantity of output produced changes.
Purely Competitive Firm
A business that operates in a market with infinite buyers and sellers, no barriers to entry, and a standard product, leaving the company as a price taker.
Q7: If events A and B are mutually
Q14: The Laspeyres index and the Paasche index
Q28: A continuous probability distribution having a rectangular
Q35: We have just performed a one-way ANOVA
Q43: Different levels of a factor are called
Q44: The sample standard deviation s is an
Q51: The _ hypothesis will be accepted only
Q65: Find a 98 percent confidence interval for
Q93: The _ assumption requires that all variation
Q121: A local tire dealer wants to predict