Use this information for questions that refer to the United Tools case.
Terry Harter is marketing manager for United Tools and Mike O'Reilly is the firm's logistics manager. They work together to make decisions about how to get United's hand and power tools to its customers - a mix of manufacturing plants and final consumers (who buy United tools at a hardware store) . United Tools does not own its own transport facilities and it works with wholesalers to reach its business customers.
Together, Harter and O'Reilly try to coordinate transporting, storing, and product handling activities to minimize cost while still achieving the customer service level their customers and intermediaries want. This usually requires that United keep an inventory of most of its products on hand, but demand for its products is fairly consistent over time so inventory is easy to manage.
Harter has identified four options for physical distribution systems she could use to reach two of her key wholesalers, Ralston Supply and Ricotta Tool Co. The total cost for each option--and the distribution service levels that can be achieved--are as follows: 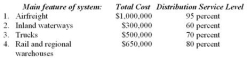 Ralston Supply expects a very high level (90 percent) of distribution customer service. Ricotta Tool Co. is willing to settle for a 70 percent customer service level, even if that means some products will occasionally be out of stock, if it gets products at a lower price.
Ralston Supply expects a very high level (90 percent) of distribution customer service. Ricotta Tool Co. is willing to settle for a 70 percent customer service level, even if that means some products will occasionally be out of stock, if it gets products at a lower price.
For its large retail hardware customers (like Home Depot) , United regularly ships smaller orders directly to individual stores or in some cases to the retail chain's warehouses. Cross-country shipments usually go by rail while regional shipments usually go by truck.
-To help in managing excess inventory, United Tools would most likely use:
Definitions:
Differential Organization
involves the varying structures and functions within an organization that contribute to its overall operation.
Distinct Group
A collection of individuals who are differentiated from others by unique characteristics, values, or behaviors.
Concentric Zone Model
A sociological model that describes urban land use in concentric circles, theorizing how social groups are spatially arranged in cities.
Urban Growth
The process by which cities expand in terms of population and infrastructure, often associated with economic development and migration from rural areas.
Q24: Transporting cost as a percentage of selling
Q27: Regrouping activities adjust the quantities or assortments
Q35: During the SALES DECLINE stage of the
Q93: The money spent to improve quality should
Q119: Agent wholesalers operate at relatively low cost--sometimes
Q181: Low transporting cost is not the only
Q184: In the United States, warehouse clubs such
Q213: Dolly Westin calls on the many gift
Q233: The _ step in the new-product development
Q318: Most catalog retailers, like Macy's and L.L.